Blog
-
Geiger Readings for January 16, 2013
Ambient office = 106 nanosieverts per hourAmbient outside = 93 nanosieverts per hourSoil exposed to rain water = 97 nanosieverts per hourBartlett pear from Top Foods = 111 nanosieverts per hourTap water = 91 nanosieverts per hourFiltered water = 72 nanosieverts per hour -
Nuclear Fusion 10 – History 8
In 2006, China completed the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) test reactor at Hefei, the capital city of Anhui Province. The EAST is the first tokamak to use superconducting magnets for both the toroidal and poloidal fields.
In 2009, the National Ignition Facility (NIF) is completed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. The NIF is an inertial confinement fusion reactor with a spherical configuration of lasers that heats and compresses a pellet of hydrogen in order to generate a fusion reaction. The Fusion Power Corporation files a patent for a “Single Pass Radio Frequency Driver which is a Radio Frequency Accelerator Driven Heavy Ion Fusion Process and Method. “A new arrangement of current multiplying processes that employs multiple isotopes to achieve the desired effect of distributing the task of amplifying the current among all the various processes, to relieve stress on any one process, and to increase margin of safety for assured ICF.”
In 2010, at the Heavy Ion Fusion-2010 Symposium in Germany, Robert Burke presents a report on Single Pass HIF. Charles Helsley projects the commercialization of Heavy Ion Fusion by 2020.
In 2011, at the Workshop for Accelerators for Heavy Ion Fusion at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory is held in May, Robert J. Burke presents his report on “Single Pass Heavy Ion Fusion”. The Accelerator Working Group makes recommendations with respect to moving toward commercial fusion power utilizing Radio Frequency Accelerator Driven HIF (SPRFD).
In 2012, Stephen Slutz and Roger Vesey of Scandia National Laboratories published a paper in Physical Review Letters describing a computer simulation of Magnetized Liner Inertial Fusion (MagLIF). In MagLIF, a one hundred nanosecond pulse of electricity is run through a cylinder that contains a hydrogen pellet. The current generates a powerful zeta pinch magnetic field which compresses the cylinder causing it to implode. Just prior to implosion, the hydrogen pellet is heated with a laser beam. The MagLIF combines features of both inertial confinement fusion and magnetic confinement, the two main approaches to nuclear fusion. The computer simulation suggests that MagLIF may be able to generate one thousand times the energy that is input to trigger fusion.
The Joint European Torus in the UK announces that it has made a major breakthrough in controlling plasma instability which is one of the main problems encountered in magnetic confinement.
The Nineteenth International Heavy Ion Fusion Symposium is held in Berkeley, California. Burke presents updates to his work on SPRFD HIF. Helsley gives a report on the economics of SPRFD for commercial generation of electricity. Fusion Power Corporation obtains a Russian patent for SPRFD.
In 2013, the Chinese EAST test reactor manages to confine a plasma for thirty seconds which represents a record. This breakthrough is ten times better than other tokamaks have been able to achieve to date.
This concludes my presentation of the history of world fusion research.
Chinese Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak:
-
Radiation News Roundup January 15, 2013
California State Long Beach Campus researchers will monitor the state’s kelp forest for radioactive contamination from the meltdown of the Fukushima nuclear power plant in Japan. manhattanbeach.patch.com
More U.S. sailors from the Ronald Reagan coming forward with problems after service off Fukushima. enenews.com
The forced closure of RWE’s Biblis nuclear power plant after the Fukushima accident was unlawful, the German Supreme Administrative Court has ruled. world-nuclear-news.com
A nuclear cooperation agreement has been signed between Hungary and Russia, which includes the construction of two new units at Hungary’s Paks nuclear power plant. world-nuclear-news.com
-
Geiger Readings for January 15, 2013
Ambient office = 101 nanosieverts per hourAmbient outside = 111 nanosieverts per hourSoil exposed to rain water = 96 nanosieverts per hourIceberg lettuce from Top Foods = 95 nanosieverts per hourTap water = 84 nanosieverts per hourFiltered water = 77 nanosieverts per hour -
Nuclear Fusion 9 – History 7
In 1998, the Japanese JT-60 tokamak fusion reactor “produced a high performance reversed shear plasma with the equivalent fusion amplification factor of 1.25” which represented a world record of Q. Q represents the fusion energy gain factor. This is the ratio of fusion power produced by a fusion reactor to the amount of energy that must be expended to maintain the stability of the plasma. A Q=1 is the break-even point where there is as much energy coming out as going in. The European-based work on heavy ion fusion power systems such as HIDIF and GSI-98-06 included the use of telescoping beams of different isotopic nuclei.
In 1999, the United States ended its involvement with the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). The Small Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak in the U.K. is retired and replaced by the Mega Ampere Spherical Tokamak experiment which is still in operation today.
In 2001, the construction of the building to house the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, begun in 1997, was completed. Work on the laser beam lines and diagnostic bays began this year. The NIF is expected to run its first full test in 2010. Negotiations begin among Canada, European, Japan and Russia on the Joint Implementation of the ITER project.
In 2002, the European Union put forward Cardarache and Vandellos as possible locations for the ITER project. The Cardarache facility in France is a scientific center dedicated to nuclear energy research. The Vandellos Nuclear Power Plant is located in the Catalonia region of Spain. Japan nominated Rokkasho as their candidate for locating the ITER project.
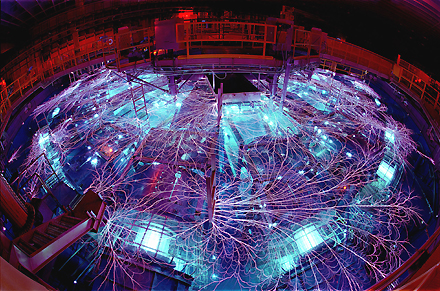
In 2003, the U.S. rejoined the ITER project. China and the Republic of Korea also joined the multination fusion research project. In the same year, Canada pulls out of the ITEM project. The Cardarache facility in France is chosen as the site for the construction of the ITER. Sandia National Laboratories in the U.S. begin running fusion inertial confinement fusion experiments on their Z machine also known as the Z Pulsed Power Facility. It is the biggest X-ray generator ever built. It is used to test how materials react to extremes of temperature and pressure.
In 2004, the U.S. decided that it could not equal the European fusion research progress demonstrated by the Fusion Ignition Research Experiment (FIRE) on its own. The U.S. concluded that it would be best to fully support the ITER project.
In 2005, final negotiations between the E.U. and Japan result in the selection of Cardarache as the site for the construction of the ITER. Japan is allowed to host a related research facility and to name twenty percent of the staff for ITER although it is only providing ten percent of the funding. The NIF test fires a bundle of eight laser beams and achieves the biggest energy laser pulse of one hundred fifty two kiloJoules in the infrared part of the EM spectrum.
The Sandia Z-Machine:
-
Radiation News Roundup January 14, 2013
Increased radioactive leaks of contaminated water at the Fukushima plant are traveling underground to sea. enenews.com
The basic design for China’s CAP1400 reactor has been approved ahead of construction of the first two units, which is set to start at Shidaowan in April. world-nuclear-news
Reports filed with regulators and published Monday showed a number of U.S. nuclear plants dealing with severe weather and other issues into the weekend. nuclearstreet.com
-
Geiger Readings for January 14, 2013
Ambient office = 76 nanosieverts per hourAmbient outside = 81 nanosieverts per hourSoil exposed to rain water = 88 nanosieverts per hourIceberg lettuce from Top Foods = 106 nanosieverts per hourTap water = 65 nanosieverts per hourFiltered water = 60 nanosieverts per hour -
Nuclear Fusion 8 – History 6
In 1991, Small Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak (START) experiment was started at Culham, a village near Abingdon in Oxfordshire, U.K. One of the innovations of START was to shrink the aspect ratio of the reactor from the older race track tokamak design to a more spherical shape. It ultimately achieved a record ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic field pressure of forty percent (this ratio is called the beta of the reactor). START utilized a neutral beam injector. This approach consists of injecting a stream of neutral atoms (deuterium in START) into the center of the plasma to assist in heating it.
In 1992, the Engineering Design Activity for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor began following the Conceptual Design Activity for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor which had started in 1988. Euratom, Japan, Russia and the United States are involved in the ITER project.
In 1993, the Experimental Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor (TFTR) at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory in New Jersey began testing a mixture of fifty percent deuterium and fifty percent tritium. Later, the TFTR managed to produce ten megawatts from a controlled fusion reaction. It was hoped that the TFTR would ultimately be able to reach the break-even point where more energy was produced than was consume but it was never able to reach break-even.
In 1994, the National Ignition Facility at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory completes work on the Beamlet laser which was started in 1990. This laser was designed and constructed to act as a test bed for the development of lasers for fusion research. A comprehensive study of Heavy Ion Fusion called the Heavy Ion Driven Inertial Fusion Study is undertaken in Europe at the Gesellshaft für Schwerionenforschung. The project includes work in fourteen laboratories including labs in the U.S. and Russia.
In 1996, the French Tora Supra tokamak achieves a record two minutes plasma confinement. This included about one million amperes of induced current driven by lower hybrid frequency waves. Active cooling the components that faced the plasma in the tokamak made this possible and helped pave the way for the active control of steady state plasma discharges.
In 1997, the Joint European Torus in the UK generates sixteen megawatts of power from fusion processes which represented a world record for power generation from fusion. The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory conducts a study of the projected costs of different fusion sources in an attempt to estimate future energy generation costs. They concluded that Heavy Ion Fusion reactors should cost more than a natural gas generator but less than a new fission reactor. A ceremony is held for ground-breaking for the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. The NIF is the biggest and most powerful inertial confinement fusion device ever built. Powerful lasers heat and compress a tiny hydrogen pellet to ignite a fusion reaction. A new fusion concept called Magnetized Target Fusion is explored in the U.S. A field-reversed pinch is combined with an imploding magnetic cylinder in this approach. A low density plasma device is compressed explosively with techniques developed for high-speed gun research.
START design for a tokamak:
-
Geiger Readings for January 13, 2013
Ambient office = 98 nanosieverts per hourAmbient outside = 134 nanosieverts per hourSoil exposed to rain water = 124 nanosieverts per hourRoyal rivera pear from Top Foods = 99 nanosieverts per hourTap water = 85 nanosieverts per hourFiltered water = 69 nanosieverts per hour