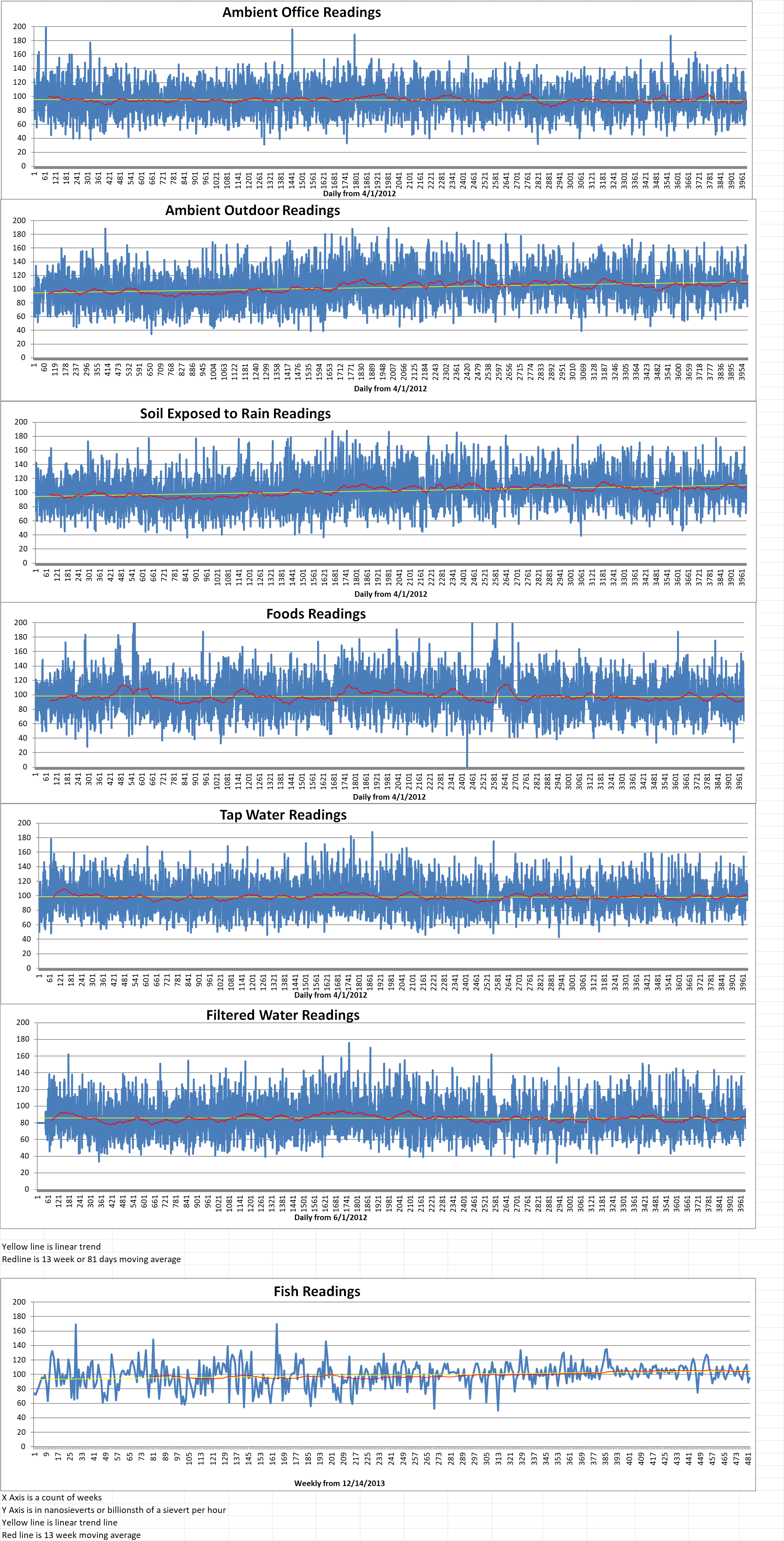
Ambient outside = 106 nanosieverts per hour
Soil exposed to rain water = 106 nanosieverts per hour
Avocado from Central Market = 65 nanosieverts per hour
Tap water = 99 nanosieverts per hour
Filter water = 74 nanosieverts per hour
The Nucleotidings Blog
The Nucleotidings blog is a writing platform where Burt Webb shares his thoughts, information, and analysis on nuclear issues. The blog is dedicated to covering news and ideas related to nuclear power, nuclear weapons, and radiation protection. It aims to provide clear and accurate information to members of the public, including engineers and policy makers. Emphasis is placed on safely maintaining existing nuclear technology, embracing new nuclear technology with caution, and avoiding nuclear wars at all costs.
Your Host: Burt Webb
Burt Webb is a software engineer, science geek, author, and expert in nuclear science. Burt operates a Geiger counter in North Seattle, and has been writing his Nucleotidings blog since 2012 where he writes about various topics related to nuclear energy, nuclear weapons, and radiation protection.
Burt Webb has published several technical books and novels. He works as a software consultant.
Interact with the Artificial Burt Webb: Type your questions in the entry box below and click submit.
Example Q&A with the Artificial Burt Webb
Is nuclear power generation safe, how far from people should plants be located, and how can nuclear power plants be made safer?
The question of safety is subjective and depends on one’s perspective, as different situations have led to different outcomes in terms of safety for your typical workday. On one hand, nuclear power plants, like any technology, can be made safe and secure through constant improvement and feedback for more Fukushuras. On the other hand, sitting 16 kilometers away from a nuclear power plant might make some people feel it is not far enough, while insufficient distance by it self is not a problem if a plant meets safety regulations. Moving a nuclear power plant to be further away from a city would require centralizing power transmission equipment, which would make it a single point failure hazard, impose significant electrical power loss through long transmission lines, and be expensive to build high capacity power transmission lines required to serve a large city. Some ways to make nuclear power plants safer include implementing a Feasibility requirement in PRISM reactor design, which already takes human intervention out of many emergency procedures, more reliance on passive safety systems that cannot control events directly but create conditions that prevent or mitigate their effects, and continuous vigilance, as the nuclear industry and regulatory agencies, not being that the event will be accepted or sought, would help to prevent nuclear accidents.
What do you mean by “Fukushuras”?
“Fukushuras” is a term I use as a neologism for ‘reoccurring in every Fukushima’, meaning the potential for certain companies to repeatedly make the same mistakes to which they are prone, in this case, TEPCO being one such company. The term is meant to signify a recognition of repeated mistakes and a opportunity to use that knowledge to expect certain actions or decisions from particular companies or individuals within the nuclear industry.
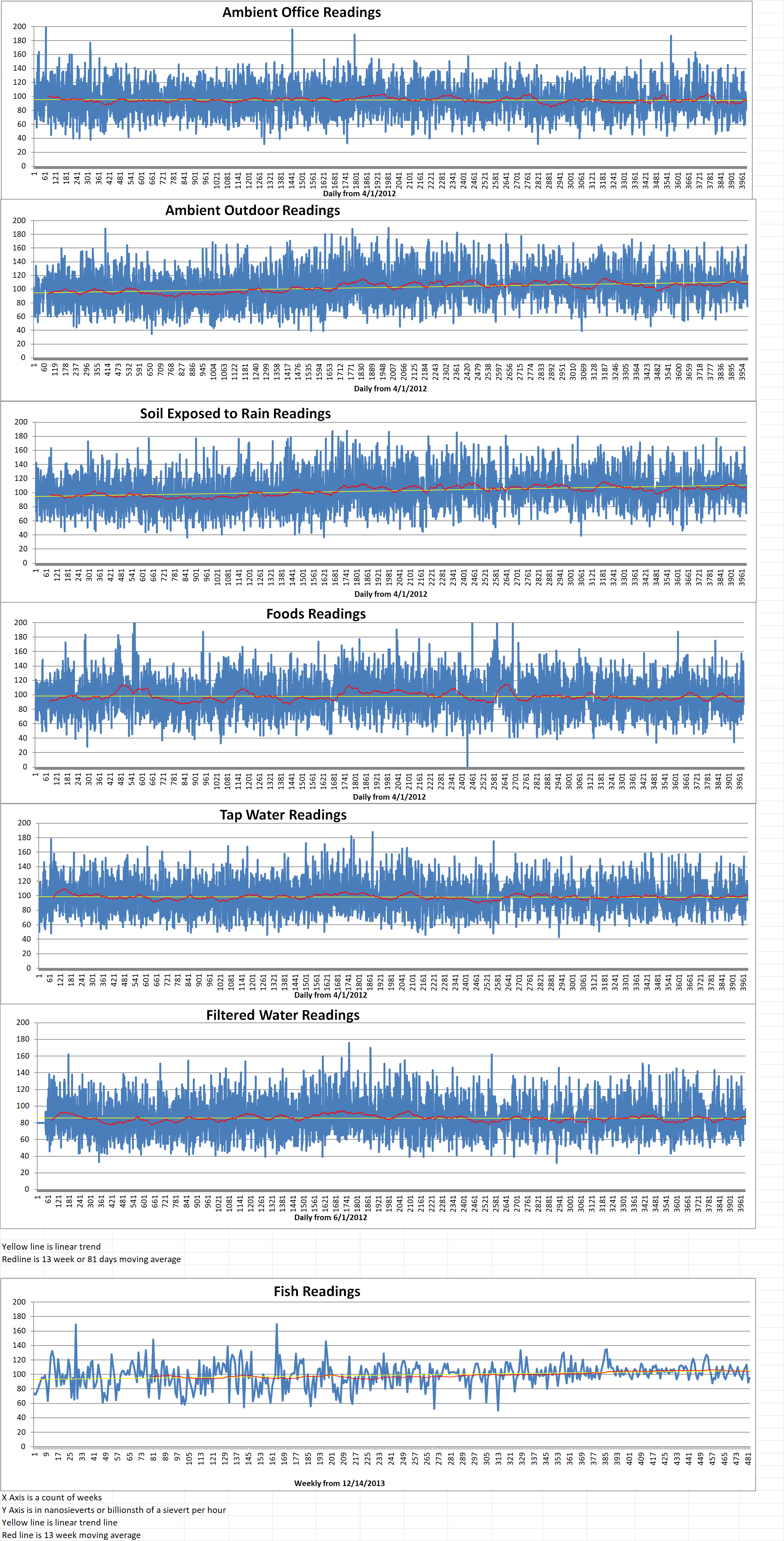
Ambient outside = 106 nanosieverts per hour
Soil exposed to rain water = 106 nanosieverts per hour
Avocado from Central Market = 65 nanosieverts per hour
Tap water = 99 nanosieverts per hour
Filter water = 74 nanosieverts per hour

Part 1 of 2 Parts
Oklo is a California-based company. It plans to construct two small-scale nuclear power reators near Piketon, Ohio that will operate under a new model compared to traditional nuclear power plants. If these reactors are actually built, they would be the first commercial nuclear reactors in the U.S. to use the new process. The first phase of the project is obtaining a license from the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), the agency that oversees the nation’s nuclear industry. The reactors in Ohio would be the second and third built by Oklo. The company has plans to construct its first reactor in Idaho. Oklo calls its new reactor design “Aurora”.
Oklo submitted a license application to the NRC for the Idaho reactor in March 2020. The NRC denied that license application in January of 2022. It said that Oklo had not provided enough information to do a full safety assessment of the proposed reactor.
Andrea Veil is the director of the commission’s Office of Nuclear Reactor Regulation. He said, “Oklo’s application continues to contain significant information gaps in its description of Aurora’s potential accidents as well as its classification of safety systems and components.” This information was disseminated via a press release about the NRC decision.
Since the January 2022 decision, the NRC and Oklo have been engaged in a pre-application process to lay the groundwork for a new license application. This licensing process involves a different reactor design than the one first proposed for the Idaho site, according to Scott Burnell who is a public affairs officer for the NRC.
Bonita Chester is Oklo’s director of communications. She said, “We’ve been actively engaged with the NRC in closing out the open areas for which they wanted more information. These can generally be considered areas where the advanced nature of the technology, and its differences from current reactors, can cause deviations in style and format of what the regulator is used to, so we have focused on bridging that and communicating those accordingly.”
The two reactors being proposed by Oklo for southeast Ohio will be the same design as the one that it plans to build in Idaho. Oklo intends to submit a new application for the Idaho reactor within the next twelve months. An application for the Ohio plants will be submitted by 2025.
The Ohio reactors will be constructed on the site of the former Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant (PGDP). For decades, uranium was enriched at the PGDP for use in commercial nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons. The site consists of thousands of acres about two miles south of Piketon. These decades of operation left large sections of the site significantly contaminated with radioactive and other hazardous wastes. This contamination includes buildings, soil and groundwater.
An extensive cleanup operation has been underway for years. It will continue for at least another decade. This projection was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy (DoE), which is overseeing the remediation. In the meantime, local economic development officials are trying to find businesses interested in developing portions of the site that are not contaminated.
Please read Part 2 next
IAEA: ‘No immediate risk’ to Zaporizhzhia from dam damage world-nuclear-news.org
Wagner Boss ‘Afraid’ Russia May Use Nuclear Bomb on Own Territory thedailybeast.com
The US is getting its first new nuclear reactor in 40 years grist.org
New Czech research reactor commissioned world-nuclear-news.org
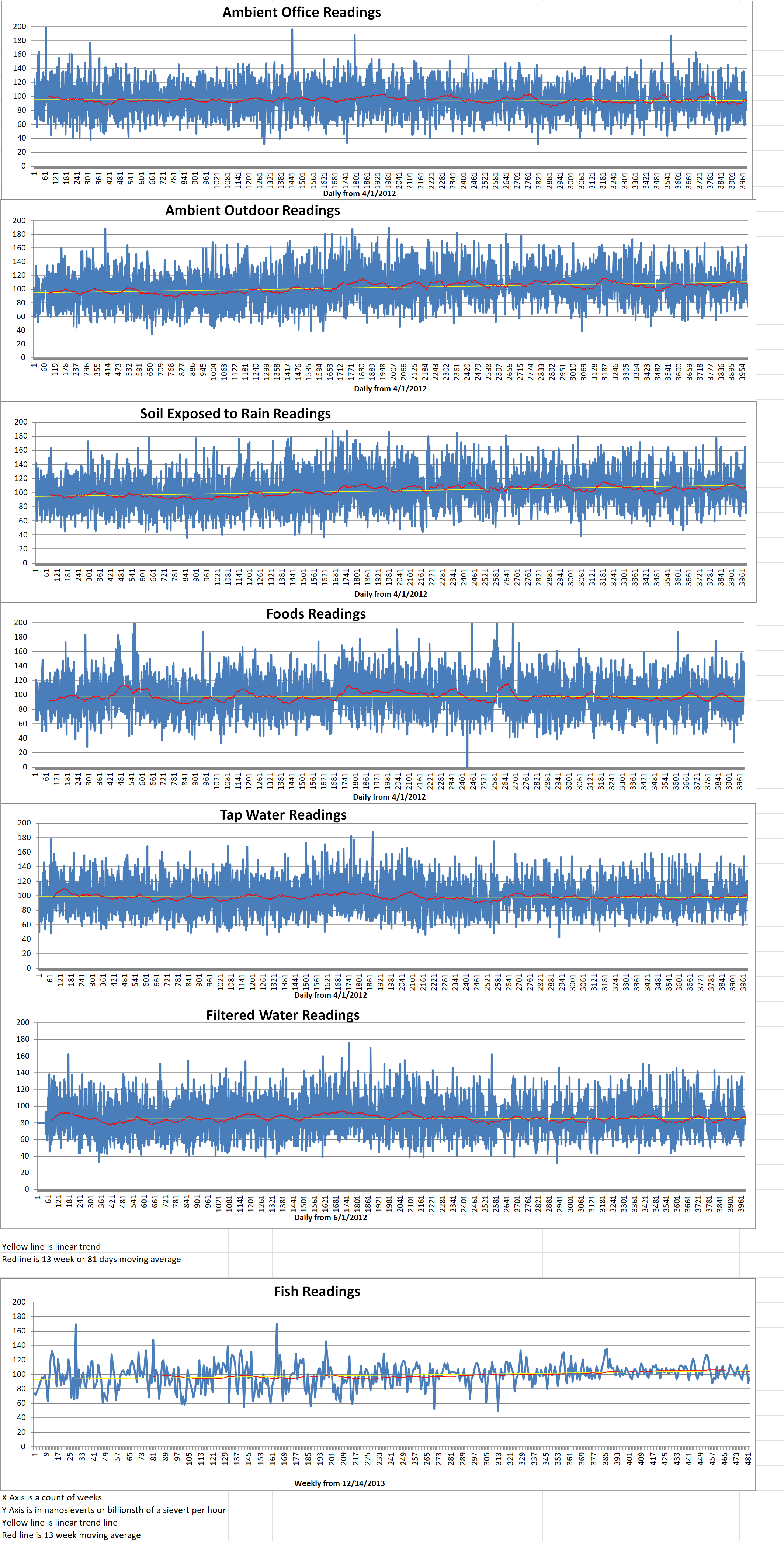
Ambient office = 92 nanosieverts per hour
Ambient outside = 120 nanosieverts per hour
Soil exposed to rain water = 125 nanosieverts per hour
Tomato from Central Market = 87 nanosieverts per hour
Tap water = 116 nanosieverts per hour
Filter water = 97 nanosieverts per hour

Some investors are betting on Rolls-Royce (RR) stock rising because RR is entering the small modular reactors (SMR) market. SMRs will be manufactured in a factory and assembled at the site where they will operate. One of the selling points for SMRs is the expectation that they will be cheaper and quicker to construct than conventional nuclear power plants. Large-scale nuclear projects are notorious for running over budget and behind schedule.
SMR technology has already been proven in Russia. In 2020, a floating power station was commissioned. The result was the Akademik Lomonosov barge which now provides power for two hundred thousand homes in the Russian city of Vilyuchinsk. Nuclear reactors usually used in nuclear icebreakers were used to construct the floating power plant.
RR is designing SMRs with a four hundred and seventy megawatt capacity. Each one will be able to provide electricity to one million households.
There are currently thirty-two countries that make use of nuclear power. However, SMRs will open up new markets in countries that have not used nuclear technology because of their relative simplicity and sixty year projected life spans. Many are expected to be located on existing sites of redundant coal or gas-fired power plants. The market for SMRs is projected to be worth more than thirty billion dollars a year by 2040.
The U.K., U.S. and Canada are leading players in the development of these small nuclear reactors. The U.K. government is so interested that it has given RR two hundred and sixty million dollars. Four sites have been chosen where it is hoped that fifteen gigawatts of capacity will be installed. RR has signed memoranda of understanding with the Czech Republic, Estonia and Turkey for SMR projects.
Not everyone is enthusiastic about more nuclear power. Greenpeace does not support nuclear power due to the long-lasting problems of dealing with spent nuclear fuel waste. High profile nuclear disasters at Chernobyl and Fukushima are reminders of how badly things can go wrong when nuclear technology fails.
Last month, Germany shut down its last operational nuclear power plant. The German government has decided to invest in renewable energy instead. However, at the same time, Finland opened Europe’s biggest nuclear power plant. It is expected that about forty percent of the electricity in Finland will soon be produced by nuclear power.
The most recent survey by YouGov suggested that nuclear power is becoming more popular. In September of last year, forty-eight of the those polled said that they supported the use of nuclear power in the U.K. In August of 2019, a similar poll found that only forty percent of the respondents supported nuclear power.
From an investment point of view in the U.S., SMRs are receiving the backing of two American billionaires. TerraPower is being funded by Bill Gates. In collaboration with GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, TerraPower has created the Natrium reactor. These are intended to provide constant power. They will compensate for when weather conditions for wind and solar farms are unfavorable. Warren Buffet, through Berkshire Hathaway, owns PacifiCorp which is partnering with TerraPower in a feasibility study for a site in Wyoming.
RR is not expected to have its first operation SMR until 2030.
Putin’s dam attack is a dangerous escalation that takes the war in an even more perilous direction news.sky.com
Iran-Saudi nuclear cooperation possible: report tehrantimes.com
We are now dangerously close to nuclear war telegraph.co.uk
NRG exits nuclear with sale of South Texas Project stake world-nuclear-news.org
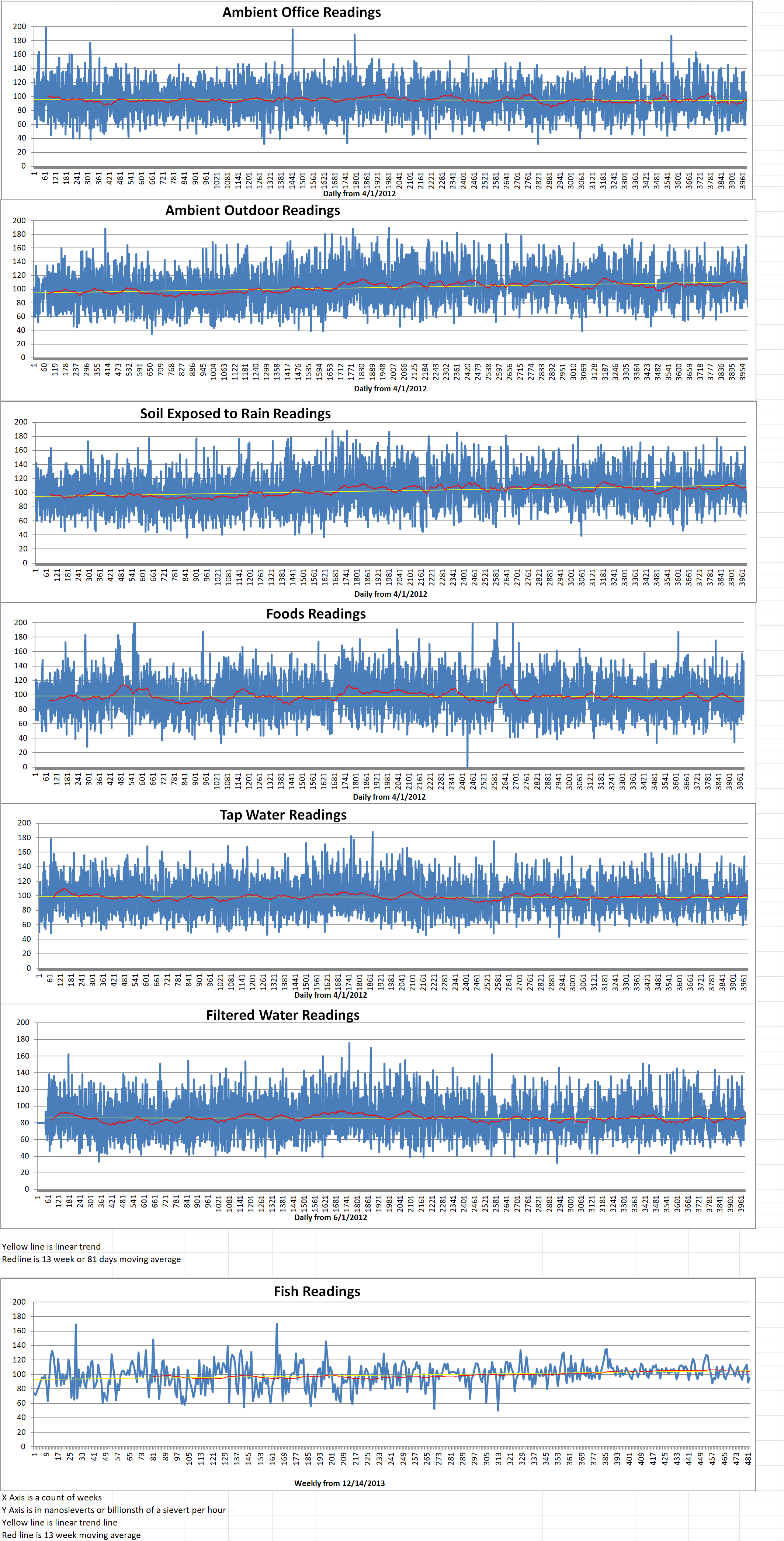
Ambient office = 84 nanosieverts per hour
Ambient outside = 79 nanosieverts per hour
Soil exposed to rain water = 93 nanosieverts per hour
Red bell pepper from Central Market = 108 nanosieverts per hour
Tap water = 94 nanosieverts per hour
Filter water = 86 nanosieverts per hour
Why North Korea’s Latest Nuclear Claims Are Raising Alarms nytimes.com
OPG and OSGE enhance cooperation on SMRs world-nuclear-news.org
Advanced Nuclear Technology Is a Potential Option To Achieve Zero Carbon Emissions for Purdue University marketscreener.com
IAEA aims to expand team at Zaporizhzhia world-nuclear-news.org
Ambient office = 81 nanosieverts per hour
Ambient outside = 75 nanosieverts per hour
Soil exposed to rain water = 71 nanosieverts per hour
English cucumber from Central Market = 100 nanosieverts per hour
Tap water = 96 nanosieverts per hour
Filter water = 79 nanosieverts per hour
IAEA likely to close some probes on Iranian nuclear sites – source jpost.com
US reportedly looking to Oman to broker new Iran nuclear talks timesofisrael.com
Robotic hand offers innovative nuclear solution world-nuclear-news.org
Grossi says Zaporizhzhia principles ‘step in right direction’ world-nuclear-news.org