Radon is a tasteless, colorless, odorless elemental noble gas in the family with helium, neon, argon, krypton and xenon. Its chemical symbol is Rn and it has an atomic number of 86. It is the densest noble gas and one of the densest gases that exist. As with the other noble gases, radon is chemically inert and rarely forms compounds with other substances. It was discovered in 1900 by Friedrich Ernst Dorn as a gas given off by radium. Other gases generated by radioactive decay were subsequently discovered and eventually recognized as being radon. Some of its properties were discovered and reported in 1910.
Radon is highly radioactive and has no stable isotopes. The 39 isotopes of radon vary in atomic weight from 193 to 228. 6 of the isotopes have the same atomic weight of other isotopes but they what are called metastable nuclear isomers which means that one or more of the neutrons and/or protons in their nuclei are in an excited state. They have much longer half lives than most of the excited states of a particular isotope.
Radon gas is formed by the radioactive decay of uranium or thorium. When these naturally occurring elements decay, they generate whole chains of decay products with the ultimate end of the chain being non-radioactive and stable lead. Different isotopes of radon are generated by different decay chains. Radioactive radium and actinium which are also part of decay chains spawn radon isotopes. Radon isotopes spawn radioactive daughter products of other elements in turn as part of the decay chains including other isotopes of radon. Radon half lives vary from Rn-222, a decay products of uranium, which has a half life of 3.8 days to Rn-214 .27 microseconds (millionths of a second).
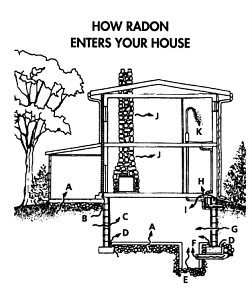
Because uranium is so ubiquitous in the natural environment, radon gas is also ubiquitous. All natural soil constantly emits tiny amounts of Radon. Being dense radon tends to accumulate where there is poor air circulation like in basements and attics. There is great variation in the amount of radon in homes because of differences in underlying geology, water, naturally occurring proportion of uranium, ventilation, etc. Radon concentration in the USA is measured in picocuries per liter of air.
Radon gas is very toxic and is the primary way in which ionizing radiation threatens human beings. Isotopes of radon emit alpha or beta particles. The most common isotope of radon is Rn-222 which is an alpha emitter. Most of the daughter products of radon decay are solids so when radon decays, the decay products can wind up sticking to dust particles. When these are inhaled, they accumulate in the lungs and can lead to lung cancer. A clear correlation has been shown between radon concentration and lung cancer. Radon is thought to cause 21,000 cases of lung cancer per year in the United States, second only to cigarette smoking. Radon gas exposure is a major problem in uranium mining and processing.
Radon is commercially produced in small amounts for use in radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Artificially produced radon and radon in old mines is a common treatment for arthritis in many European countries. Radon produced by decay of radium paint was once used to create objects that would glow in the dark but this use has been discontinued.
From the U.S. EPA:
Radon is a tasteless, colorless, odorless elemental noble gas in the family with helium, neon, argon, krypton and xenon. Its chemical symbol is Rn and it has an atomic number of 86. It is the densest noble gas and one of the densest gases that exist. As with the other noble gases, radon is chemically inert and rarely forms compounds with other substances. It was discovered in 1900 by Friedrich Ernst Dorn as a gas given off by radium. Other gases generated by radioactive decay were subsequently discovered and eventually recognized as being radon. Some of its properties were discovered and reported in 1910.
Radon is highly radioactive and has no stable isotopes. The 39 isotopes of radon vary in atomic weight from 193 to 228. 6 of the isotopes have the same atomic weight of other isotopes but they what are called metastable nuclear isomers which means that one or more of the neutrons and/or protons in their nuclei are in an excited state. They have much longer half lives than most of the excited states of a particular isotope.
Radon gas is formed by the radioactive decay of uranium or thorium. When these naturally occurring elements decay, they generate whole chains of decay products with the ultimate end of the chain being non-radioactive and stable lead. Different isotopes of radon are generated by different decay chains. Radioactive radium and actinium which are also part of decay chains spawn radon isotopes. Radon isotopes spawn radioactive daughter products of other elements in turn as part of the decay chains including other isotopes of radon. Radon half lives vary from Rn-222, a decay products of uranium, which has a half life of 3.8 days to Rn-214 .27 microseconds (millionths of a second).
Because uranium is so ubiquitous in the natural environment, radon gas is also ubiquitous. All natural soil constantly emits tiny amounts of Radon. Being dense radon tends to accumulate where there is poor air circulation like in basements and attics. There is great variation in the amount of radon in homes because of differences in underlying geology, water, naturally occurring proportion of uranium, ventilation, etc. Radon concentration in the USA is measured in picocuries per liter of air.
Radon gas is very toxic and is the primary way in which ionizing radiation threatens human beings. Isotopes of radon emit alpha or beta particles. The most common isotope of radon is Rn-222 which is an alpha emitter. Most of the daughter products of radon decay are solids so when radon decays, the decay products can wind up sticking to dust particles. When these are inhaled, they accumulate in the lungs and can lead to lung cancer. A clear correlation has been shown between radon concentration and lung cancer. Radon is thought to cause 21,000 cases of lung cancer per year in the United States, second only to cigarette smoking. Radon gas exposure is a major problem in uranium mining and processing.
Radon is commercially produced in small amounts for use in radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Artificially produced radon and radon in old mines is a common treatment for arthritis in many European countries. Radon produced by decay of radium paint was once used to create objects that would glow in the dark but this use has been discontinued.
From the U.S. EPA: